
RPA (Robotic Process Automation) Consultant in Singapore
Contact UsWhat is RPA (Robotic Process Automation) Consulting?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) consulting involves the strategic implementation of software robots, or 'bots', designed to automate highly repetitive and rule-based tasks that are usually performed by humans. These bots operate on PCs or virtual machines and are programmed to execute tasks by mimicking user actions. They follow defined business logic and structured steps to complete processes efficiently.
RPA consulting specifically focuses on identifying, customising, and managing these automation solutions to optimise company processes, increase operational efficiency, and reduce costs. The goal is to free up human resources from mundane tasks so they can focus on more complex and strategic activities that require human judgement and interaction.
RPA consulting specifically focuses on identifying, customising, and managing these automation solutions to optimise company processes, increase operational efficiency, and reduce costs. The goal is to free up human resources from mundane tasks so they can focus on more complex and strategic activities that require human judgement and interaction.
What Can Be Automated with RPA Consulting & Implementation Services?
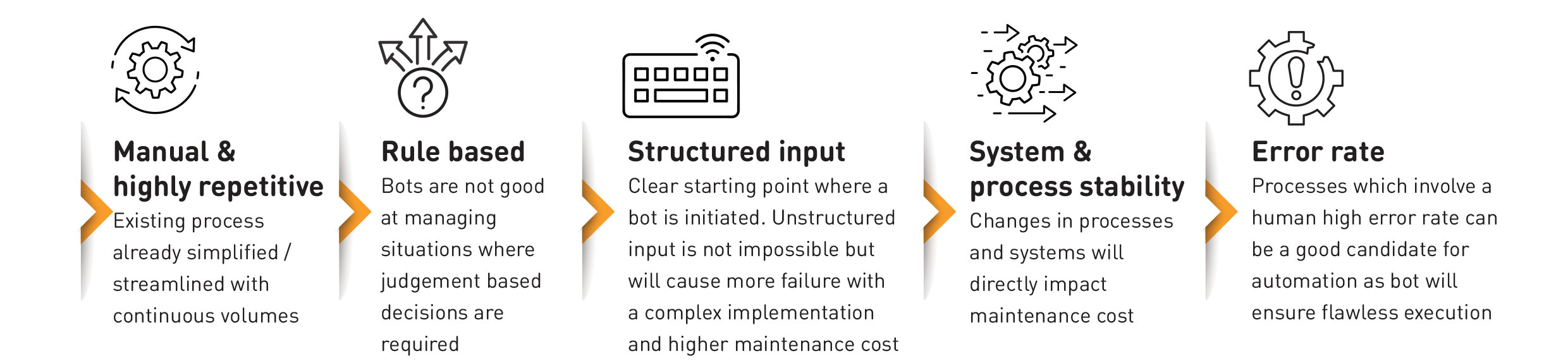
The Manual & Highly Repetitive
Rule-Based Processes
Structured Inputs
Overly-lengthy system processes
Processes Involving High Human Error Rates
Benefits of Working with Robotic Process Automation Consultants
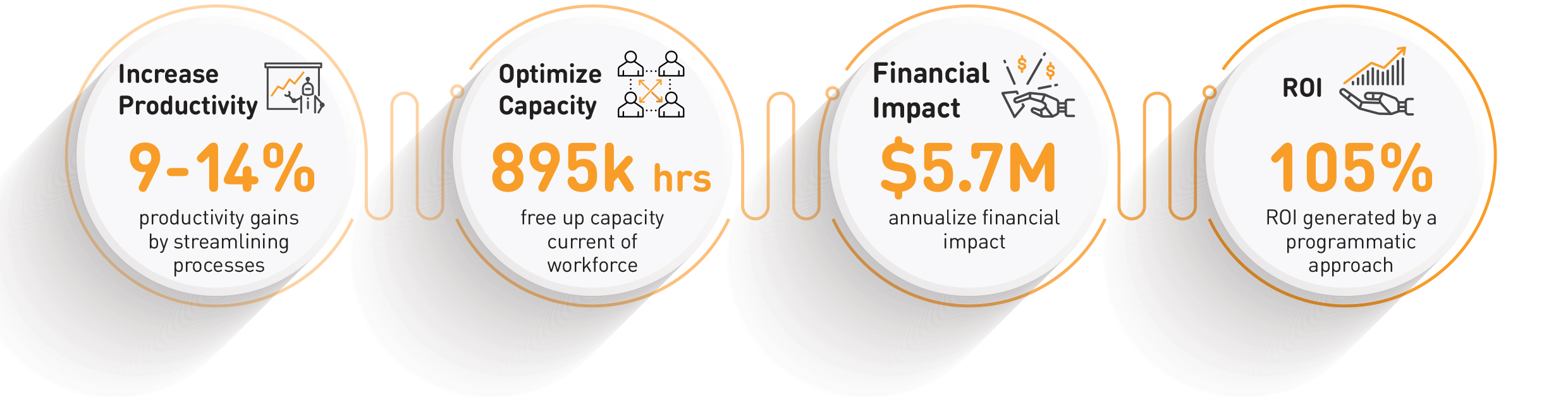
Increase Productivity
Optimise Capacity
Create Financial Impact
Enhance ROI
How Does RPA Consultancy Work?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) consultancy is a systematic approach that transforms business processes through the strategic deployment of software robots. Here’s how our consultancy typically unfolds, ensuring that every phase of the process is tailored to your specific organisational needs:
First Call
Walkthrough and Discovery Session
Estimation and ROI Calculation
Use Cases of Robotic Process Automation Services
Enhancing Financial Operations
Revolutionising Customer Service
Streamlining Healthcare Administration
Optimising Supply Chain Management
FAQs about RPA Companies & Consulting Firms in Singapore
Common challenges during RPA implementation include managing change among employees, integrating RPA with existing IT systems, and scaling the bots efficiently across the company. To overcome these challenges:
Practise Change Management: Effective communication and training programmes are essential. It’s important to involve employees early in the process, educating them about the benefits of RPA and how it will enhance their work rather than replace it.
Exercise Good IT Integration: RPA should be integrated in a way that complements existing IT architectures. Collaboration with IT teams from the outset ensures that the RPA deployment aligns with the company's technology standards and protocols.
Leverage Scalability: Start with pilot projects to demonstrate the value of RPA before scaling up. This approach helps in understanding the complexities involved and planning resources accordingly for a broader deployment.
Success metrics for RPA initiatives typically include:
Cost Reduction: Measuring the decrease in operational costs post-implementation.
Accuracy and Quality Improvements: Tracking error rates before and after automation.
Productivity Gains: Assessing the increase in work output and the amount of time saved on manual tasks.
Employee Satisfaction: Gauging how RPA has affected employee job satisfaction and engagement, often through surveys and interviews.
Customer Satisfaction: Monitoring changes in customer service metrics, such as shorter response times or higher resolution rates, which can be attributed to faster and more accurate process handling.
RPA and AI are distinct but complementary technologies. RPA is primarily rule-based and is used to automate routine tasks that do not require decision-making capabilities. In contrast, AI involves machine learning and natural language processing to make decisions and learn from outcomes.
When combined, RPA can handle the automation of repetitive tasks, while AI provides intelligence to handle non-routine tasks and make complex decisions. This combination can lead to the automation of entire business processes that involve both predictable tasks and those requiring insights and adaptation, enhancing the scope and scale of automation solutions.